What is Aquaponics?
Introduction to Aquaponics
Have you ever thought about combining fish farming and gardening into one seamless system? That’s what aquaponics is all about! This innovative approach not only grows plants without soil but also incorporates aquatic life, creating a symbiotic system that’s as fascinating as it is efficient.
The Basics of Aquaponics
Definition of Aquaponics
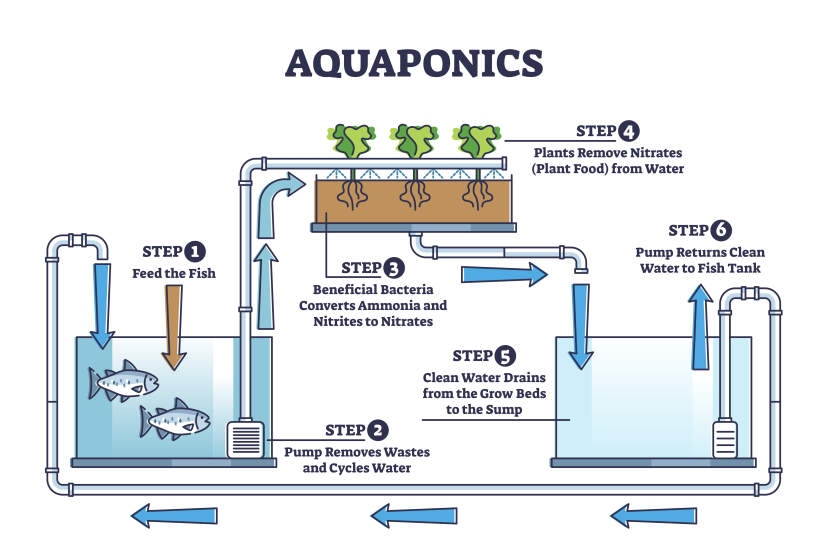
Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil). In this system, fish waste provides nutrients for plant growth, and plants help filter and clean the water for the fish. It’s a win-win situation for both!
Why Choose Aquaponics?
It offers a harmonious blend of productivity and sustainability. It’s perfect for anyone looking to grow their food in an eco-friendly, space-efficient manner. Plus, who wouldn’t love having a mini-ecosystem right in their backyard?
How Does Aquaponics Work?
Essential Components
To build a successful system, you’ll need these critical components:
The Fish Tank
The fish tank is the heart of the system, where your aquatic friends live and produce nutrient-rich waste.
The Sump Tank
A sump tank is an optional but useful component that acts as the lowest point in the water circulation system. It collects water from the grow beds or other parts of the system and serves as a central reservoir where water is pumped back to the fish tank.
Grow Beds
These are where your plants grow. Typically filled with a growing medium like clay pellets, grow beds act as biofilters to clean the water.
Plumbing Systems
Pipes and pumps circulate water between the fish tank and grow beds, ensuring nutrients and oxygen are distributed evenly.
Bacteria and Their Role
Beneficial bacteria convert fish waste into plant-friendly nutrients. This natural process, called nitrification, is vital to the system’s success.
Types of Aquaponic Systems
Media-Based Systems
This is the most common system, where plants grow in a medium like gravel or clay pellets, and water from the fish tank flows through it.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
In NFT systems, a thin film of water flows continuously over plant roots, providing nutrients while minimizing water use.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Plants float on a raft with their roots submerged in oxygenated nutrient water. It’s efficient and ideal for larger-scale setups.
Vertical Aquaponics
This space-saving design stacks plants vertically, making it perfect for urban or small-space gardening.
Advantages of Aquaponics
Sustainable Food Production
It allows you to grow plants and raise fish simultaneously, offering a reliable source of fresh vegetables and protein.
Water Efficiency
This system uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming, as water is recirculated and reused.
Natural Pest Control
Without soil, many common pests are eliminated. Plus, the closed system reduces exposure to external contaminants.
Dual Yield Benefits
Why settle for just plants when you can harvest fish too? This system offers double the productivity in one system.
Challenges of Aquaponics
Initial Investment Costs
Setting up this system can be expensive, especially if you’re aiming for a large-scale operation.
System Maintenance
Monitoring water quality, maintaining equipment, and ensuring a healthy balance between fish and plants require regular effort.
Balancing Fish and Plants
Keeping the fish and plants happy involves striking the right balance in nutrients, pH, and oxygen levels—a task that can take time to master.
Getting Started with Aquaponics
Choosing the Right Fish
Tilapia, trout, and goldfish are popular choices for aquaponics due to their adaptability and nutrient-rich waste.
Selecting Plants
Leafy greens like lettuce, kale, and herbs are ideal for beginners, as they thrive in nutrient-rich water.
Tips for Beginners
- Start small and scale up as you learn.
- Regularly test water quality for pH, ammonia, and nitrate levels.
- Ensure a good aeration system to keep your fish and plants healthy.
Aquaponics vs. Hydroponics
Key Differences
While both systems grow plants without soil, aquaponics integrates fish into the equation, creating a closed-loop ecosystem. Hydroponics focuses solely on plants and requires external nutrient inputs.
Which One Is Better?
It depends on your goals. Aquaponics is more sustainable and offers dual yields (plants and fish), while hydroponics is simpler to set up and maintain.
Future of Aquaponics
Role in Urban Agriculture
Aquaponics is revolutionizing urban farming, allowing fresh food production in cities where space is limited.
Advancing Sustainable Farming
As climate challenges intensify, aquaponics offers a scalable, eco-friendly solution for food security worldwide.
Conclusion
Aquaponics is an incredible fusion of nature and technology, providing a sustainable way to grow food while conserving resources. Whether you’re an aspiring urban farmer or just looking for a rewarding hobby, it is worth exploring. So, why not dive in and create your own mini-ecosystem?
FAQs
What types of fish are best for aquaponics?
Tilapia, trout, catfish, and goldfish are popular due to their hardiness and adaptability.
Is aquaponics environmentally friendly?
Yes! It uses less water, minimizes waste, and creates a sustainable loop between fish and plants.
How much space do I need for aquaponics?
This system can be adapted to small spaces, making it suitable for apartments or large-scale farms.
What plants grow well in aquaponics?
Leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, and tomatoes thrive in this system.
Can beginners start with aquaponics?
Absolutely! Start small with a simple system and build your skills over time.